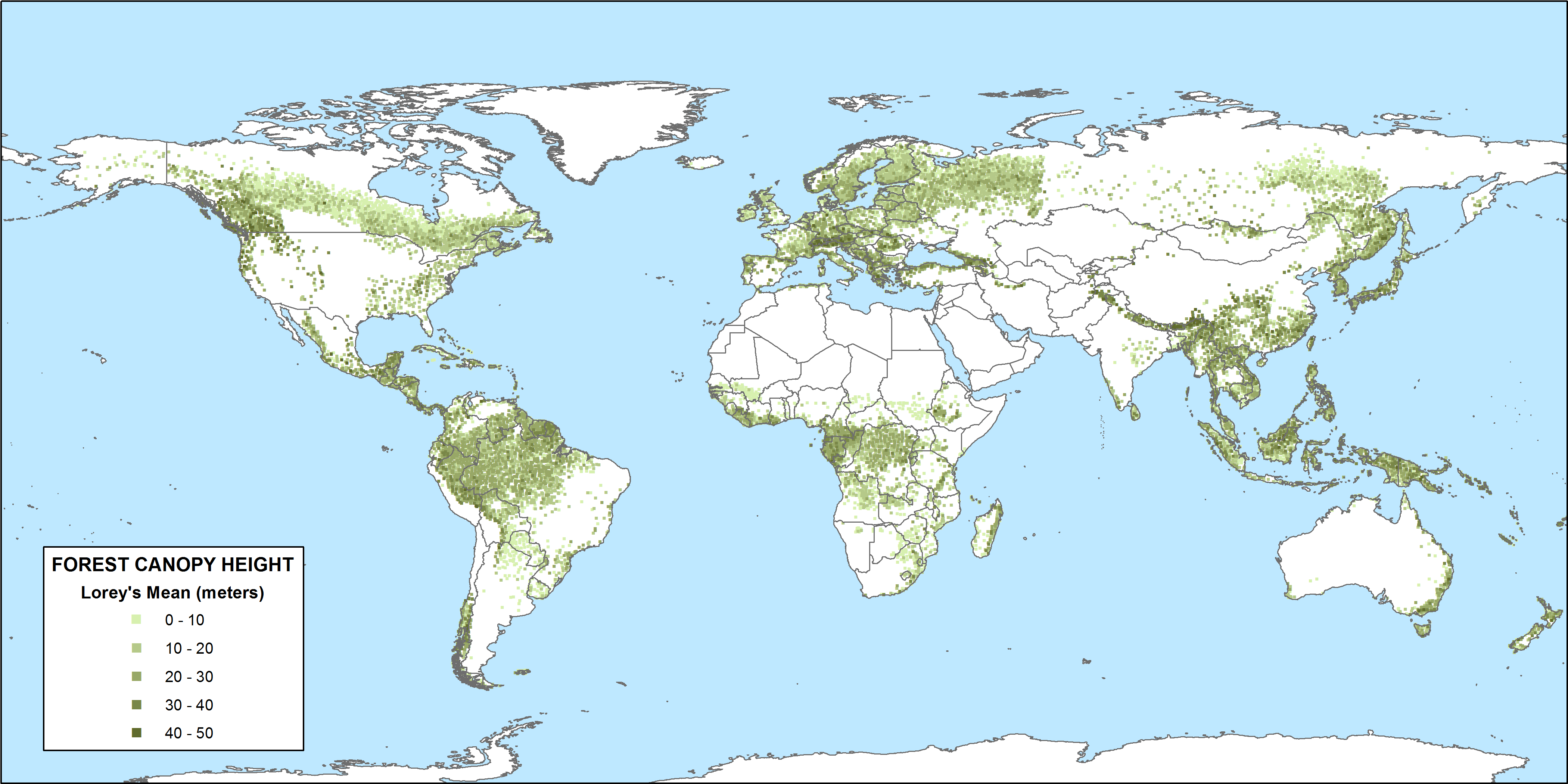
Tropical forest canopy height plays a crucial role in understanding the health and sustainability of these vital ecosystems, often referred to as the lungs of the Earth. As researchers delve deeper into the intricacies of forest dynamics using advanced NASA GEDI technology, they are uncovering alarming impacts of climate change on these towering canopies. The height of the canopy not only reflects the overall forest health but also indicates the capacity for carbon storage, a significant factor in mitigating global warming. Studies have shown that shifts in canopy measurement can provide critical insights into how trees cope with rising temperatures and prolonged dry seasons. Exploring the relationships between canopy height and environmental variables is essential for formulating effective strategies to protect tropical forests and combat climate change.
The upper layers of rainforest ecosystems, often termed the forest canopy, serve as a key indicator of ecological vitality and regional biodiversity. Utilizing breakthroughs in remote sensing technology, scientists are now more equipped than ever to analyze how climatic factors influence these towering arboreal structures. As important players in the global carbon cycle, these elevated forest zones are essential not just for their lush vegetation, but for their role in regulating atmospheric conditions. Insights into variations in canopy height allow researchers to assess the broader health of tropical woodlands and their ability to sequester carbon amidst shifting climatic patterns. By observing the interplay of various environmental factors impacting canopy structures, we can develop better conservation strategies for protecting these vital ecosystems.
The Crucial Role of Tropical Forest Canopy Height
Tropical forest canopy height serves as an essential indicator of the overall health of forest ecosystems. Taller canopies correlate with increased carbon storage capabilities, which are critical in the fight against climate change. This relationship underscores the importance of canopy measurement and monitoring, especially as we face rising global temperatures and prolonged periods of drought. According to research utilizing NASA’s GEDI LiDAR technology, variability in canopy height is influenced significantly by environmental factors, making it a focal point for scientists studying forest health and climate resilience.
In regions such as the Amazon, Africa, and Southeast Asia, variations in canopy height reflect the adaptive strategies of these forests against climate changes. Studies indicate that taller canopies not only store more carbon but also play a pivotal role in regulating local temperatures and microclimates. Increased understanding of canopy dynamics is vital for developing effective conservation strategies that mitigate the impacts of climate change. As we delve deeper into the environmental drivers of canopy height, we can better comprehend the intricate relationships within these ecosystems.
Impact of Climate Change on Tropical Forests
Climate change poses a significant threat to the health of tropical forests worldwide. The prolonged dry seasons, primarily observed in regions like the southern Amazon, have led to a measurable reduction in canopy height. According to studies published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the impact of climate change on forest health is not uniform across different regions. The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) has played a crucial role in identifying how climate variables such as solar radiation and elevation contribute to variations in canopy height.
Understanding the climatic influences on canopy structure not only assists in evaluating current forest health but also aids in predicting future changes. As researchers continue to utilize advanced technology like NASA’s GEDI, they can provide essential insights into how tropical forests may evolve with ongoing climate shifts. Protecting these vital ecosystems is fundamental in our collective response to climate change, emphasizing the need for targeted conservation efforts that prioritize the most vulnerable regions.
Significance of NASA’s GEDI Technology
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) has revolutionized our understanding of forest dynamics through advanced LiDAR measurements. By capturing detailed vertical profiles of the forest canopy, GEDI enables scientists to assess the structure and health of tropical forests on an unprecedented scale. This technology has transformed the way researchers measure forest characteristics, moving from localized studies to a global perspective. The ability to capture comprehensive data across diverse ecosystems is vital as we strive to understand the intricate effects of climate change.
Through GEDI, researchers have uncovered critical insights into the drivers of forest canopy height and how these factors relate to carbon storage and ecosystem productivity. For instance, changes in canopy height have been linked to climatic variables such as moisture levels and dry seasons. By leveraging this technology, scientists can better predict how tropical forests will respond to ongoing climate pressures, ultimately informing policy decisions aimed at conservation and carbon management in these essential ecosystems.
Forest Health and Ecosystem Productivity in Tropical Regions
Forest health is a key indicator of ecosystem productivity, especially in tropical regions where biodiversity and carbon storage are exceptionally high. Tall canopies are often indicative of robust ecosystem functions, including enhanced carbon sequestration, which plays a critical role in mitigating climate change. Monitoring the health of tropical forests helps in understanding their ability to withstand environmental stressors and maintain their ecological balance. By prioritizing forest health assessments, we can develop more effective conservation strategies and ensure the sustainability of these ecosystems.
Ecosystem productivity in tropical forests not only supports wildlife but also provides significant economic resources for local communities. Healthy forests yield timber, non-timber forest products, and recreational opportunities, contributing to both environmental and human well-being. Therefore, ensuring the vitality of tropical forest ecosystems is essential for maintaining their biodiversity, climate resilience, and the livelihoods that rely on them.
Environmental Drivers of Canopy Height Variation
The study of environmental drivers affecting canopy height variation in tropical forests reveals critical insights into forest responses to climate dynamics. Factors such as topography, soil characteristics, and climatic conditions underscore the complexity of forest ecosystems. Researchers have identified that nearly three-quarters of the variability in canopy height can be explained by these environmental variables, making them key focal points for ongoing studies. This understanding is crucial for assessing the carbon storage potential and conservation value of different tropical forestry regions.
Before utilizing technologies like NASA’s GEDI, researchers were limited in their capacity to analyze large swaths of forest land. Now, with advanced LiDAR capabilities, scientists can examine not only the structural aspects of canopy height but also the underlying environmental conditions that dictate these variations. Such knowledge empowers conservationists and policymakers to develop strategies that enhance the resilience of tropical forests against climate change.
The Future of Tropical Forest Conservation
The future of tropical forest conservation hinges on our ability to address the impacts of climate change while promoting sustainable practices. As new data emerges from technologies like NASA’s GEDI, it sheds light on the vulnerabilities of various forest ecosystems. Understanding how climate variables affect canopy height and, consequently, forest health is essential for creating effective mitigation strategies. Policymakers and conservationists must prioritize areas that show signs of stress and are likely to suffer from prolonged dry seasons or extreme weather events.
Moreover, as we move forward, integrating scientific findings into policy decisions will be vital in the preservation efforts of these unique ecosystems. By recognizing the urgent need for conservation and restoration of tropical forests, we can leverage current research to build awareness, educate communities, and mobilize resources for protective measures. This holistic approach to understanding and acting upon the environmental challenges facing tropical forests will be crucial in combating climate change for generations to come.
Tropical Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Tropical forests are renowned for their incredible biodiversity, housing more than half of the Earth’s terrestrial species. This biodiversity not only contributes to the ecological stability of the planet but also provides invaluable ecosystem services such as carbon storage, water regulation, and soil fertility. Maintaining healthy tropical forests is essential for preserving this biodiversity, which in turn supports agricultural productivity and provides resources for local and global economies.
However, the increasing pressures from climate change, deforestation, and urbanization threaten these vital ecosystems. By utilizing research from NASA’s GEDI and other studies, scientists can monitor the health and status of tropical ecosystems, leading to more effective conservation strategies. Protecting the rich biodiversity of tropical forests not only ensures the survival of countless species but also sustains human livelihoods that depend on these ecosystems.
Monitoring Canopy Changes with Remote Sensing Technology
Remote sensing technology, particularly NASA’s GEDI, has transformed the way researchers monitor changes in tropical forest canopies. By providing high-resolution data on canopy structure, this technology allows scientists to gauge the health of forests and assess the implications of climate change over broad geographical areas. The detailed insights gained from remote sensing enable a more informed understanding of canopy dynamics, essential for forming effective forest management strategies.
Through continuous monitoring of canopy heights and health, researchers can track ecological changes over time. This data-driven approach aids in identifying patterns related to climate variables, ultimately facilitating better predictions of future canopy variations. By embracing these advanced scientific methodologies, conservationists can design targeted actions to protect and restore tropical forest ecosystems under threat from climate change.
The Role of Canopy Measurement in Mitigating Climate Change
Canopy measurement plays a pivotal role in our efforts to mitigate climate change by providing insights into the carbon sequestration capabilities of tropical forests. As these ecosystems are critical in absorbing atmospheric CO2, understanding their canopy structure and health can greatly influence climate policy decisions. Research using technologies like NASA’s GEDI enhances our knowledge of how various factors affect canopy height and the associated carbon dynamics within these forests.
By emphasizing the importance of canopy measurement, we can derive strategies that prioritize forest conservation and restoration initiatives. This not only helps maintain biodiversity but also reinforces carbon storage functions vital for global climate health. As we confront increasing environmental challenges, the need for focused research and policy development in the context of canopy measurement becomes clear, ensuring that tropical forests continue to act as effective carbon sinks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of tropical forest canopy height in understanding forest health?
Tropical forest canopy height is a crucial indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity. Taller canopies typically signify higher carbon storage and greater above-ground biomass, which play essential roles in sequestering carbon and mitigating climate change.
How does NASA’s GEDI technology measure tropical forest canopy height?
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) uses spaceborne LiDAR technology from the International Space Station to measure tropical forest canopy height. This technology enables detailed assessments of the vertical structure and leaf density of forest canopies across extensive areas, previously limited to smaller local studies.
What environmental factors affect tropical forest canopy height and how do they relate to climate change?
Environmental factors such as climate, topography, and soil properties significantly impact tropical forest canopy height. Particularly, the study revealed that prolonged dry seasons due to climate change can reduce canopy heights, especially in vulnerable regions like the southern Amazon.
How does the height of tropical forest canopies influence climate and local ecosystems?
Tropical forest canopy height is vital because it helps buffer microclimates and can reduce temperatures during heat waves. Taller canopies not only support greater biodiversity but also enhance carbon sequestration, making them an integral part of strategies to combat climate change.
What insights did NASA GEDI provide regarding variations in tropical forest canopy height?
NASA GEDI revealed that nearly three-quarters of the variation in tropical forest canopy height can be attributed to climate, topography, and soil. The study highlighted that factors like elevation and solar radiation are significant in determining canopy height across various tropical regions.
Why are tropical forests considered essential for carbon sequestration and climate policy?
Tropical forests are critical for carbon sequestration as they store vast amounts of carbon, which helps mitigate climate change. Understanding their canopy heights and health is vital for devising effective climate policies and conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of these biodiversity hotspots.
What challenges do tropical forests face due to climate change, according to the latest studies?
Recent studies indicate that tropical forests face challenges such as longer dry seasons and increased drought frequency due to climate change, which can lead to significant reductions in canopy height and disrupt the overall health of these ecosystems.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Tropical Forest Canopy Height | The upper layer of trees in tropical forests, critical for ecosystem health. |
| Importance of Canopy Height | Indicates forest health, carbon storage capacity, and influences microclimate. |
| Impact of Climate Change | Climate change affects canopy height; prolonged dry seasons can reduce height. |
| Study Utilization of Technology | NASA’s GEDI LiDAR technology enabled vast measurements of canopy height variations. |
| Regions Studied | Pacific regions in Asia, Africa, and South America with minimal disturbance. |
| Environmental Factors | Elevation, dry season length, and solar radiation significantly impact height variance. |
| Future Research | Researchers aim to expand studies to more forest areas to inform policy for conservation. |
Summary
Tropical forest canopy height is a crucial indicator of forest health and biodiversity. Recent studies using advanced NASA LiDAR technology have unveiled significant insights into how climate change affects this vital metric. By examining environmental factors such as elevation, dry season duration, and solar radiation, researchers found that these variables account for most variations in canopy heights across tropical regions. As climate change continues to alter precipitation patterns and increase the length of dry seasons, particularly in vulnerable regions like the southern Amazon, it is essential for policymakers to prioritize the protection of tropical forests for both their carbon storage capabilities and ecological significance.