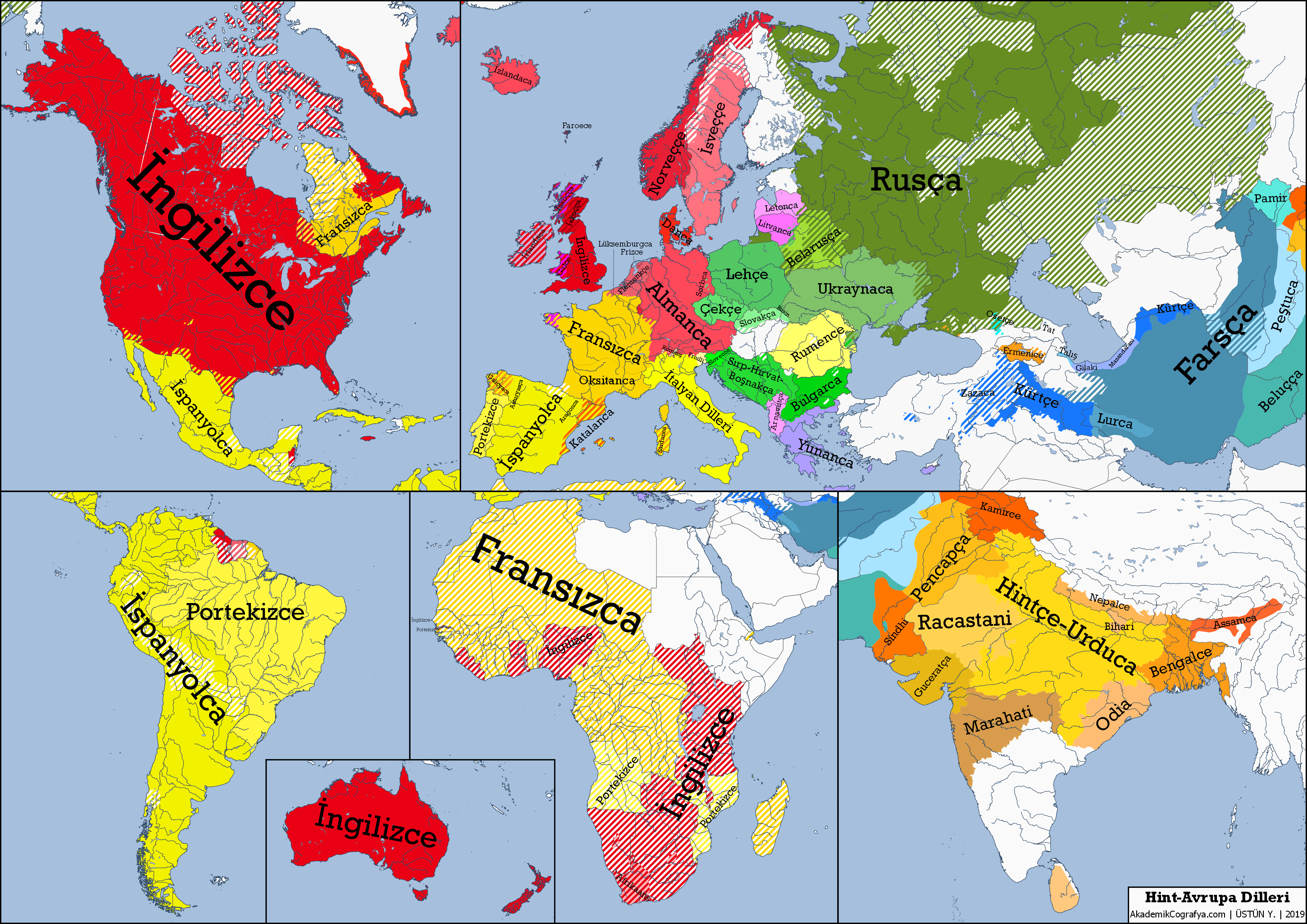
Indo-European languages, comprising a vast family of over 400 languages spoken by nearly 40% of the world, may trace their origins back to a significant cultural and genetic interplay that unfolded in ancient Eurasia. Recent groundbreaking studies have pinpointed these proto-Indo-European speakers to present-day Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. This research connects the early Yamnaya people, who thrived in the steppe regions along the lower Volga River and near the Caucasus Mountains, to the evolutionary paths of these languages. Through ancient DNA analysis, researchers reveal how the Yamnaya mingled with various populations, shaping linguistic traditions that would traverse vast distances, from Europe to the Indian subcontinent. By uncovering these roots, scholars strive to unravel the linguistic tapestry that has influenced countless languages and cultures across the globe.
The exploration of linguistic families, particularly the Indo-European languages, unveils a fascinating narrative rooted in the migrations and interactions of ancient peoples. Utilization of terms like ‘proto-languages’ and ‘linguistic ancestry’ reflects the intricate evolution of these language systems over millennia. The Yamnaya culture, often highlighted in discussions of early Indo-European origins, serves as a pivotal point in understanding how early pastoralist societies contributed to language dissemination across regions. Studies leveraging ancient DNA research further illuminate the genetic ties that form the foundation of modern European and Asian languages, enriching our comprehension of historical linguistics. This examination not only sheds light on vocabulary origins but also on the broader cultural exchanges that have shaped human communication.
The Roots of Proto-Indo-European Languages
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) languages form the backbone of a rich linguistic family that not only includes widely spoken languages such as English, Spanish, and Hindi, but also ancient ones like Latin and Sanskrit. The origins of these languages have puzzled linguists and historians for centuries, as they represent a tapestry woven across vast geographic landscapes. Recent studies have pinpointed the speakers of this ancestral language to a specific timeline and location, suggesting that around 6,500 years ago, the proto-Indo-European speakers flourished in the steppes of Eurasia, specifically near the Lower Volga River in present-day Russia.
The transformative role of the Yamnaya people in the development and diffusion of these languages cannot be overstated. Their nomadic lifestyle and innovative adoption of technologies, such as horse riding and cart usage, catalyzed their movement across Europe and into Asia. As the Yamnaya migrated, they took their language with them, influencing the linguistic landscape of the regions they settled in. This dissemination was not merely a spread of words; it entailed a complex interaction with indigenous populations, leading to the emergence of diverse dialects and languages that would eventually evolve into what we recognize today.
The Yamnaya’s Role in Language Evolution
The Yamnaya culture, characterized by its pastoralist lifestyle around 3000 BCE, served as a crucial node in the spread of the Indo-European languages. They facilitated this linguistic evolution through their extensive trade networks and intercommunity interactions. As they navigated across diverse terrains, their language began to assimilate various local dialects, leading to the gradual emergence of new language forms. Research indicates that the Yamnaya were not only transmitters of culture but also benefactors of genetic and linguistic exchange with neighboring groups.
Their exploration extended from the steppes north of the Black and Caspian seas into parts of Europe, reaching regions as far as Mongolia and Ireland. This massive migration encapsulated a staggering spread of over 6,000 kilometers, showcasing how language travels alongside culture and genetics. Archaeological and genetic studies continue to reveal the layers of influence the Yamnaya had, ultimately uniting disparate linguistic family trees into the Indo-European branch.
Genetic Evidence from Ancient DNA Analysis
Ancient DNA analysis has revolutionized our understanding of proto-Indo-European speakers and their descendants. By examining genetic samples from archaeological sites across Russia and Europe, researchers identified markers that trace back to the Yamnaya and their contemporaries. This groundbreaking approach not only affirms linguistic theories but also provides a tangible connection to the past, allowing scientists to map the migrations of these early peoples with unprecedented accuracy.
The genetic findings align well with linguistic phenomena, supporting the theory that significant population movements facilitated the spread of Indo-European languages. For instance, notable shifts in genetic ancestry across Europe, coupled with the introduction of new linguistic branches, suggest that these ancient speakers intermingled with local populations, further diversifying the family of Indo-European languages. This genetic tapestry created a complex web of relationships that underpinned the very fabric of European and Asian languages.
Cultural Interactions and Language Spread
As the Yamnaya people migrated, their cultural practices played a pivotal role in the dissemination of the Indo-European languages. Their adoption of kurgan burials, a ceremonial practice that marked their presence across the Eurasian steppe, is not merely an archaeological footnote but a cultural marker that helped signal their linguistic identity. These burial mounds attracted attention from archaeologists over generations, emphasizing the interconnectedness of language, culture, and community practices in shaping identity.
The connections drawn from the Yamnaya’s culture indicate that language spread was not a linear process but an intricate dance of interaction among various groups. As the Yamnaya mingled with settled agriculturalists and other nomadic tribes, their language absorbed elements from these societies, enriching its structure and vocabulary. The eventual diversification of the Indo-European languages into various branches exemplifies how cultural dynamics influenced language evolution over millennia.
The Caucasus Lower Volga: The Cradle of Language
Recent studies highlight the significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga region as the cradle of Indo-European languages. Researchers posit that this area served as a melting pot of cultures that amalgamated to form the early linguistic roots of the language family. By analyzing ancient DNA and archaeological findings, it becomes evident that the interactions between the Yamnaya and other groups in this region laid the groundwork for what would evolve into a wide array of languages spanning continents.
The identification of these origins marks a significant milestone in linguistics and archaeology. The genetic evidence that links the Caucasus Lower Volga people to the spread of Indo-European languages acts as a crucial bridge connecting the modern world to its historical foundations. With every discovery, researchers unravel layers of history that illustrate how language is anchored in cultural context and migration patterns, ultimately illustrating the diverse linguistic heritage that characterizes much of the modern-day landscape.
Challenges and Breakthroughs in Linguistic Research
Despite the remarkable advances made in tracing the origins of Indo-European languages, researchers still confront numerous challenges, particularly due to geopolitical tensions. The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has hindered collaborative efforts between scholars, resulting in a divide that complicates the full understanding of the linguistic landscape. The establishment of substantial connections between ancient populations and their languages often necessitates cooperative international research efforts that are currently stymied.
Moreover, the complexities of language evolution further complicate the narrative. Linguists and geneticists are tasked with disentangling a long, intertwined history of migration, intermarriage, and cultural exchange that has occurred over thousands of years. Each new discovery serves as a reminder of how dynamic and layered human history truly is. However, the relentless pursuit of knowledge in this field is underscored by increasing breakthroughs in both genetic analysis and linguistic reconstruction that continue to shed light on our shared past.
Understanding Readability: The Intersection of Science and Language
Among the many discoveries stemming from studies of Indo-European origins is a greater understanding of how languages are structured and how they evolve. Insightful analyses reveal that languages are shaped not only by genetics but also by environmental factors and cultural practices. The readability of any given language is intricately tied to its history, and researchers are illuminating the pathways through which simplicity and complexity in language structure evolve.
Understanding the principles of readability enables linguists to draw connections between languages while also evaluating the effectiveness of communication throughout history. This focus on the scientific properties of language enhances our comprehension of both ancient and contemporary tongues, emphasizing the dynamic interplay of linguistic evolution driven by populations like the Yamnaya and their descendants.
Emerging Techniques in Linguistic Research
The landscape of linguistic research is continuously evolving, thanks to technological advancements and emerging methodologies. Genetic studies, particularly ancient DNA analysis, have introduced new dimensions to the exploration of Indo-European origins. These techniques allow researchers to create more nuanced perspectives on the relationships between genes and language, effectively merging disciplines of genetics, archaeology, and linguistics to more accurately plot the interconnections of human populations.
Furthermore, the development of computational models in linguistic analysis is revolutionizing the ways in which researchers can predict language evolution. By employing algorithms and simulations, scholars are beginning to capture intricate patterns of change that were once challenging to identify. This interdisciplinary approach is not only enriching our understanding of Indo-European languages but is also opening doors to new areas of discovery that remain fundamental to uncovering our shared linguistic heritage.
The Future of Indo-European Linguistic Research
As research into Indo-European languages expands, the future holds tremendous promise for further discoveries. The ongoing integration of genetic and linguistic evidence will likely yield even more detailed maps of linguistic evolution and migrations. Scholars are optimistic that, despite current challenges, the blending of disciplines will reveal deeper insights into how the languages that dominate today emerged from a common ancestral source.
Future studies are poised to explore uncharted territories concerning lesser-known languages that may have played a crucial role in the broader Indo-European family tree. Through advancements in technology and collaboration between researchers worldwide, the story of Indo-European languages will continue to unfold, enriching our understanding of human history and cultural identity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the origins of Indo-European languages based on recent studies?
Recent research has traced the origins of Indo-European languages to the Caucasus Lower Volga region in present-day Russia, where proto-Indo-European speakers originated around 6,500 years ago. This genetic and linguistic analysis highlights the Yamnaya people as significant contributors to the spread of these languages through cultural interaction and migration.
How did the Yamnaya people influence the spread of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya people, known for their nomadic pastoral lifestyle and advancements in horse riding, began spreading Indo-European languages around 5,000 years ago. They migrated from the steppe grasslands of the lower Volga River, expanding their territories across Europe to areas as far as Ireland and Mongolia, effectively disseminating linguistic and cultural traits.
What does ancient DNA analysis reveal about proto-Indo-European speakers?
Ancient DNA analysis has provided vital insights into the ancestry of proto-Indo-European speakers, revealing their genetic connections to the Caucasus Lower Volga people and other ancient populations. This comprehensive genetic data supports the existence of a significant mixing event that contributed to the modern European gene pool and the linguistic landscape of Indo-European languages.
What role did the Caucasus Lower Volga region play in the development of Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus Lower Volga region is identified as a crucial center for the development of Indo-European languages. It is where genetic evidence points to the prototype families of these languages, specifically highlighting their connections to both the Yamnaya and other ancient Indo-Anatolian speakers in the area.
How have the findings on Indo-European languages changed our understanding of linguistic history?
The findings from recent studies have revolutionized our understanding of linguistic history by confirming the genetic connections among Indo-European languages and their speakers. The research not only validates the steppe hypothesis but also underscores the complexity introduced by population migrations and mixing, reshaping our perspective on how these languages evolved across different regions.
What challenges do researchers face in studying the origins of Indo-European languages?
Researchers face challenges such as geopolitical tensions impacting collaborative studies, particularly regarding access to ancient DNA from conflict regions like Ukraine. These circumstances have complicated the collection of comprehensive genetic data essential for understanding the full scope of Indo-European language origins.
Why is the Yamnaya culture significant in the context of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture is significant for its role in the dispersal of proto-Indo-European languages across Europe and into parts of Asia. Their unique burial practices, societal structures, and technological innovations allowed them to influence the linguistic development profoundly, marking a pivotal moment in human history.
What evidence supports the link between Yamnaya ancestry and Indo-European languages?
Evidence supporting the link between Yamnaya ancestry and Indo-European languages includes ancient DNA analyses that trace genetic lineages from the Yamnaya through various regions where Indo-European languages have been identified. This genetic tracing serves as a ‘tracer dye,’ indicating migration patterns alongside language spread.
How do linguists and geneticists collaborate in the study of Indo-European languages?
Linguists and geneticists collaborate by integrating linguistic theories with genetic data to create a comprehensive understanding of population dynamics and language evolution. This interdisciplinary approach enhances the analysis of how ancient populations influenced the spread and development of Indo-European languages throughout history.
What are some key cultural practices of the Yamnaya people related to language development?
Key cultural practices of the Yamnaya people that relate to language development include their burial rituals in kurgans, which reflect a complex social structure. These practices, coupled with their nomadic lifestyle and intermingling with local populations, facilitated the transmission and diversification of Indo-European languages.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Identified as originating from present-day Russia about 6,500 years ago during the Eneolithic period. |
| Research Studies | Two significant studies published in Nature, revealing genetic evidence linked to the language’s origins. |
| Ancestry and Migration | The Caucasus Lower Volga people are believed to be the ancestors who spread in the region. |
| Cultural Practices | The Yamnaya culture practiced burial in kurgans, which provided archaeological insights into their society. |
| Role of Genetics | Genetic research highlighted intermingling with other groups and migrations across Europe and India. |
| Key Figure Mentioned | David Reich, a prominent researcher in human genetics, plays a key role in the studies. |
| Challenges Faced | Political tensions affecting collaborations between Russian and Ukrainian scholars during research. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a rich and complex origin, tracing back to specific ancestors who lived in what is now Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. These languages, spoken by over 40% of the global population, have evolved through intricate migrations and intermixing of cultures. The recent integration of genetic studies with linguistic research has illuminated the paths taken by these ancient peoples, revealing the interconnectedness of language and heritage across vast regions. This groundbreaking work not only resolves longstanding linguistic mysteries but also highlights the cultural and genetic heritage that shaped the Indo-European language family as we recognize it today.